New case report of rare pediatric seizure data captured with MEG.
We report in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience a rare case of ictal (seizure) MEG recording of pediatric drug-resistant epilepsy. This project was driven by Saskia van Heumen, who visited our lab virtually as an undergrad summer research trainee from @tudelft (The Netherlands). This is another successful collaboration with lab graduate Dr. JT Moreau and Dr. RWR Dudley, neurosurgeon at @HopitalChildren.
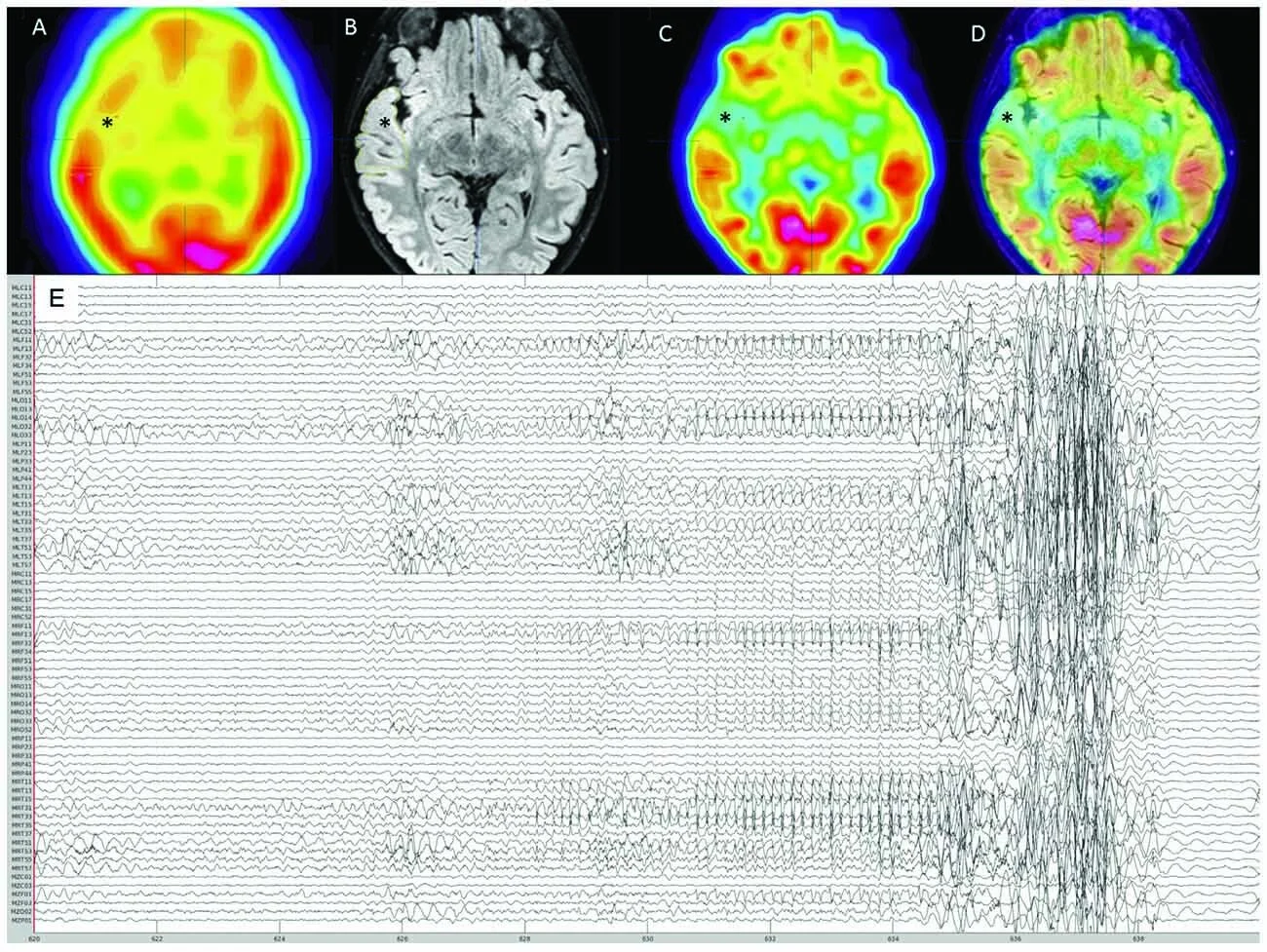
We performed a rare, 4h overnight MEG recording in an 8-yo w/ drug-resistant focal epilepsy & captured one ~45-s seizure. The patient underwent a selective right anterior temporal resection and remains seizure-free 21 months postoperatively.
The histopathological assessment confirmed frank focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) type IIa in the MEG-defined seizure onset zone (SOZ), which was based on source imaging of averaged ictal spikes at seizure onset.
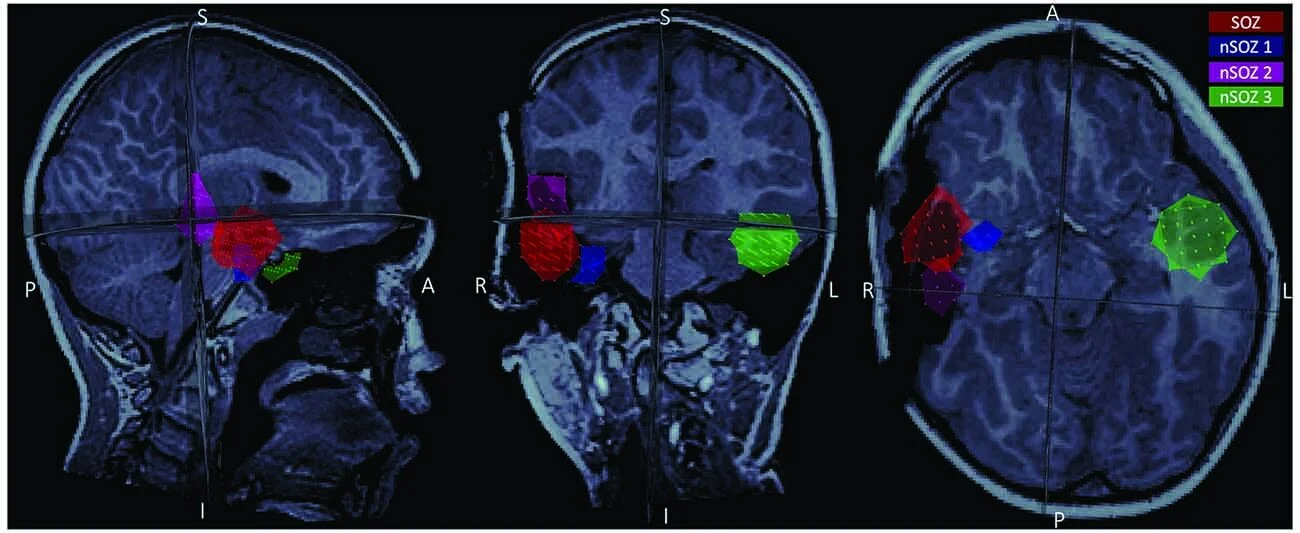
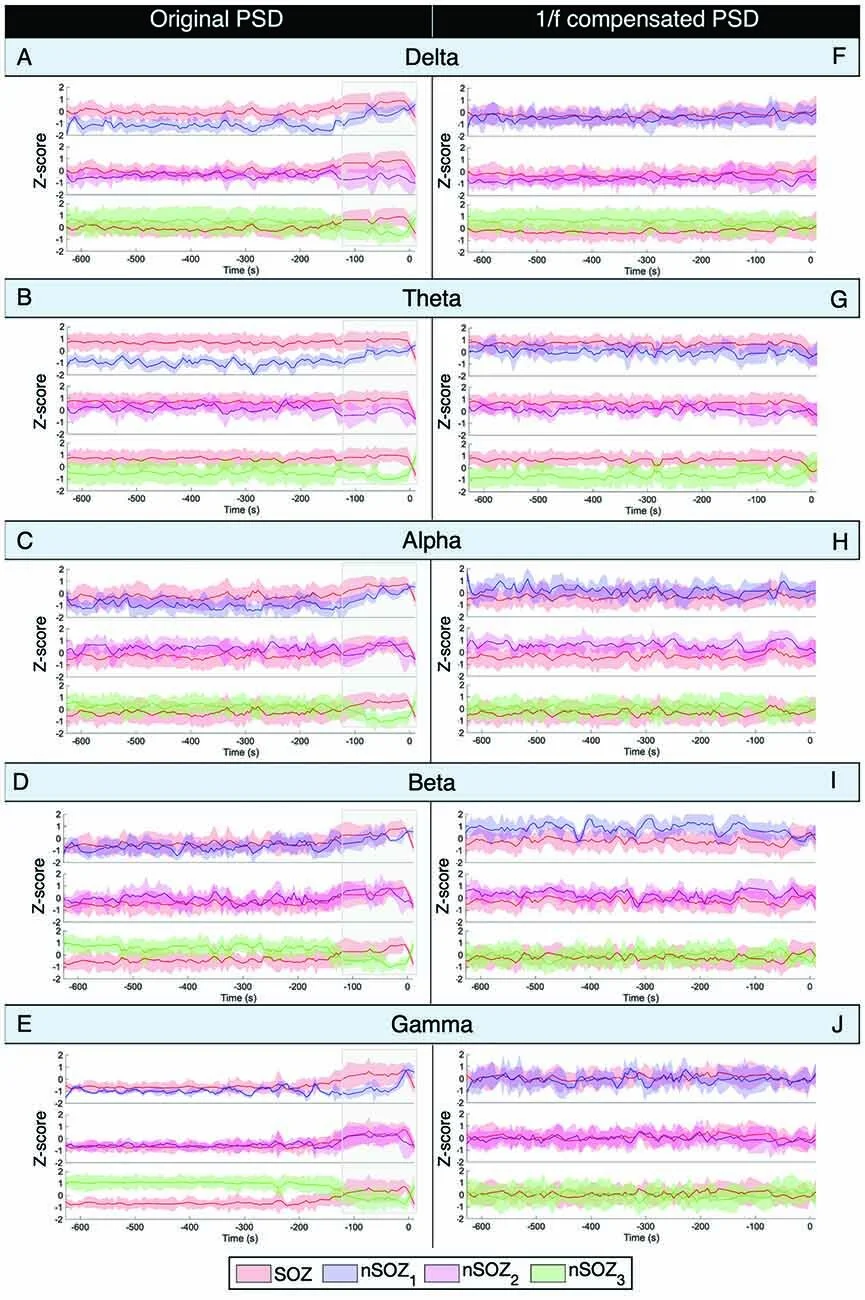
We investigated temporal changes & spatial differences (SOZ vs. control areas) in spectral parameters of background brain activity (aperiodic broadband offset & slope) & assessed how they confounded the interpretation of variations of signal power in typical frequency bands of electrophysiology.
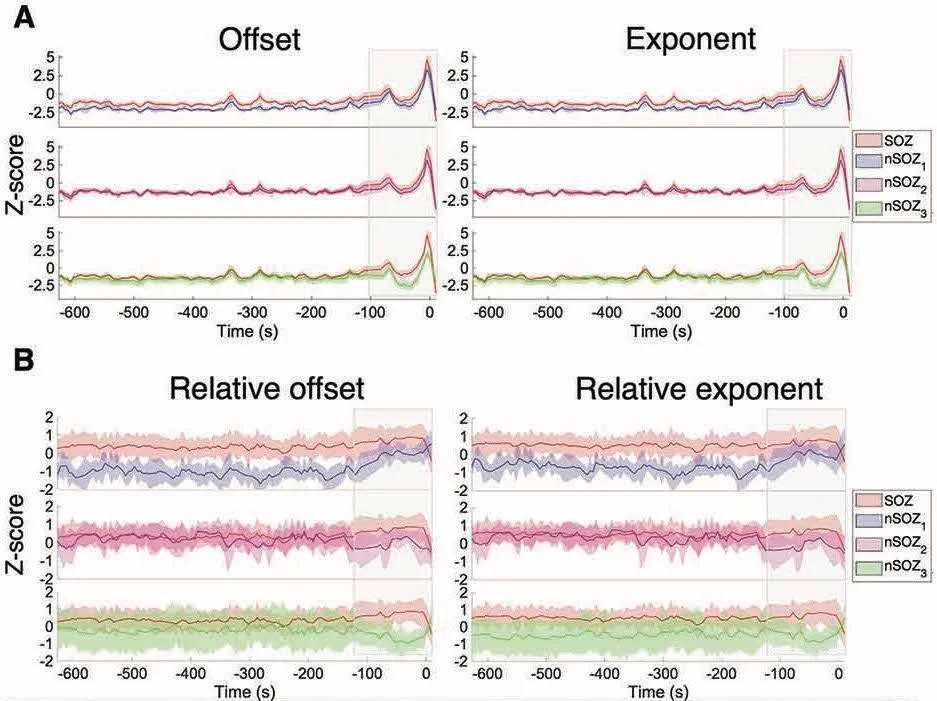
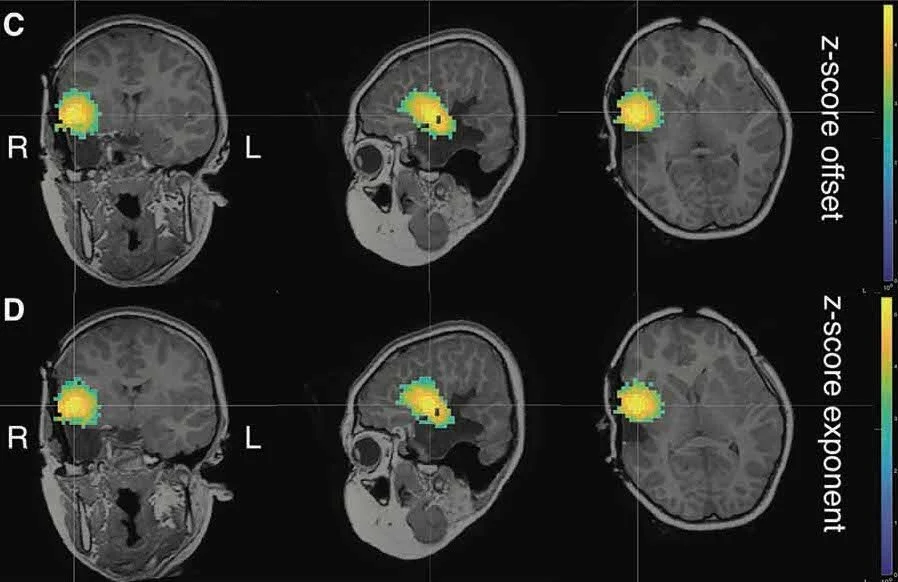
Our data show that the SOZ was associated with a higher aperiodic offset & exponent during the seizure compared to control regions. Both parameters increased in all regions from 2 min before the seizure onwards.
Regions anatomically closer to the SOZ also expressed higher values compared to contralateral regions, potentially indicating ictal spread. We also show that narrow-band power changes were caused by these fluctuations in the aperiodic component of ongoing brain activity.
Our results indicate that the broadband aperiodic component of ongoing brain activity cannot be reduced to background noise of no physiological interest, and rather may be indicative of the neuropathophysiology of the SOZ.
All analyses were performed with our software toolkit Brainstorm (free and open-source), including FOOOF decompositions of the signal frequency spectra adapted from the Voytek’s lab (UCSD).
Paper is in open access.